How to enable Course Outcomes in Moodle | Moodle 3.9
#Moodle #ELearning #PradeepKumarTS
This post is to enable Course outcomes or Learning Outcomes in Moodle Learning Management Systems. This is for Faculty Members or one who teach a course.
Steps:
1. Login to Moodle with your username and Password.
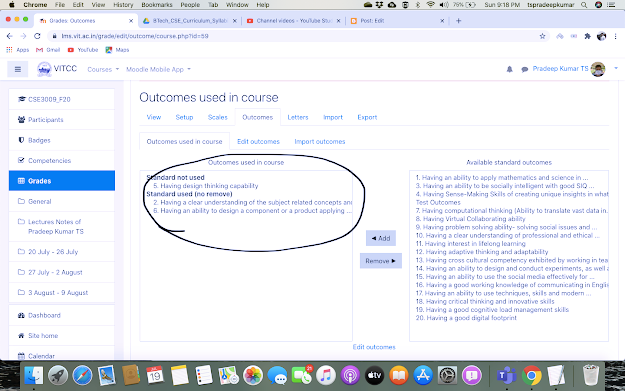
2. Go to Your Course -- Click the Settings ICON -- Click "Outcomes" and select the outcomes of your course. (there will be all course outcomes, select the three or four outcomes of your course and Click Add button so that the Outcomes will be copied from Right to Left )



sir i'm installing ns2 in ubuntu 20.04 using your video but after using ./install command I logout the pc and then try to login gain but not able to login even after entering the correct password,it's still showing me enter password and that window login window is showing again please help sir
ReplyDeleteYou might have given a empty space in the .bashrc file and remove unnecessary blank spaces in that file and try again
ReplyDeleteTo go to the window, use CTL +ALT +F2 and then using terminal mode, go to the /home//.bashrc file and do the changes and save it and exit.. You can login to your OS.